Navigating between views (iOS)¶
If your iOS app has multiple views, you can add voice commands to navigate between them. In this tutorial, we will add a new view to our starter iOS app and create commands to switch between the app views with voice.
What you will learn¶
How to send commands from the dialog script to an iOS app
How to handle commands on the iOS app side
How to navigate between views in an iOS app with voice
What you will need¶
To go through this tutorial, make sure you have completed the following tutorial: Building a voice Agentic Interface for an iOS Swift app. You can also use an example app provided by Alan AI: SwiftTutorial.part1.zip. This is an XCode project of the app already integrated with Alan AI.
Step 1: Add a new view to the app¶
Note
This step is required if you are using the starter iOS app created in the previous tutorial. You can also use your own app with several views. In this case, skip this step and go to step 2.
In the Building a voice Agentic Interface for an iOS Swift app tutorial, we have created an iOS app with a single view, and added the Alan AI agentic interface to it. Let’s add a new view to this app. We will use the Navigation Controller to manage the app views.
In Xcode, open the app’s storyboard:
Main.storyboard.In the storyboard, select the app view by clicking the view dock.
Go to Editor > Embed In > Navigation Controller. The Navigation Controller will be added to the storyboard, and the app view will be linked to it.
Go to View > Show Library to open the Library, find View Controller in it and drag it to the storyboard. Place the added View Controller element to the right of the first View Controller.
From the Library, add a button to the first View Controller and name the button, for example:
Show Second View.Select the button, press and hold the Control key on the keyboard and drag from the button to the second View Controller. In the displayed window, select Show.
Select the created segue and in the Attribute Inspector, in the Identifier field, set the ID for it:
goForward. We will use this ID later in this tutorial to switch to the second view with voice.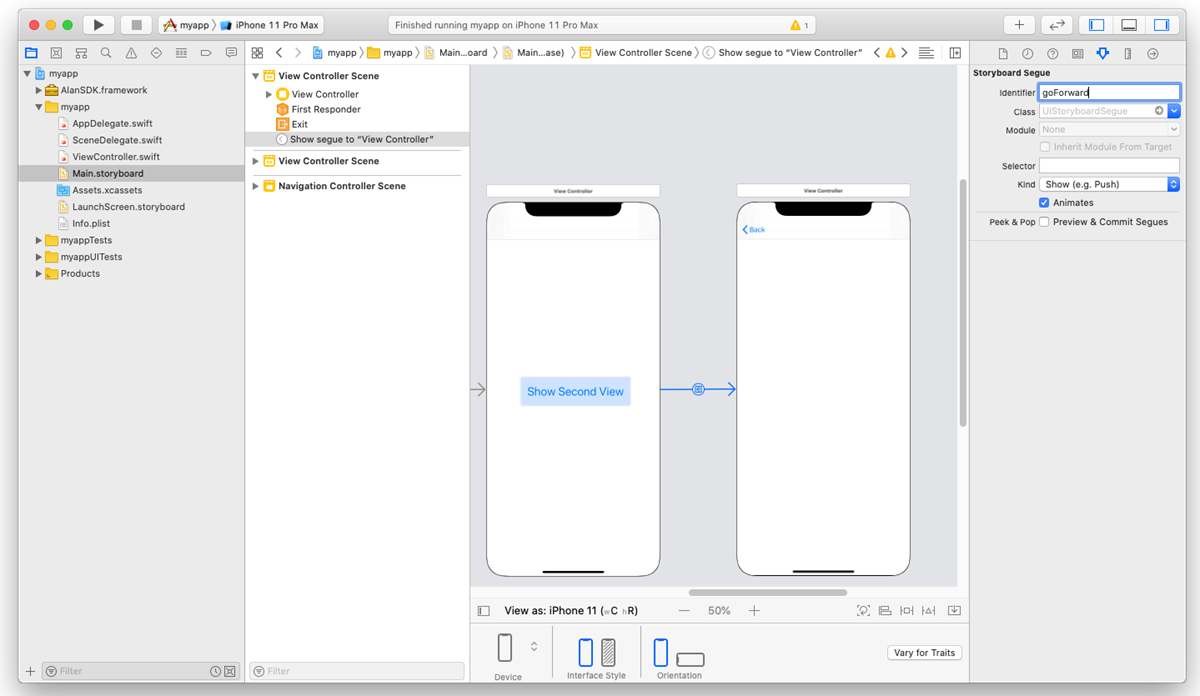
Open the
ViewController.swiftfile and replace:ViewController.swift¶class ViewController: UIViewController
with
ViewController.swift¶class ViewController: UINavigationController
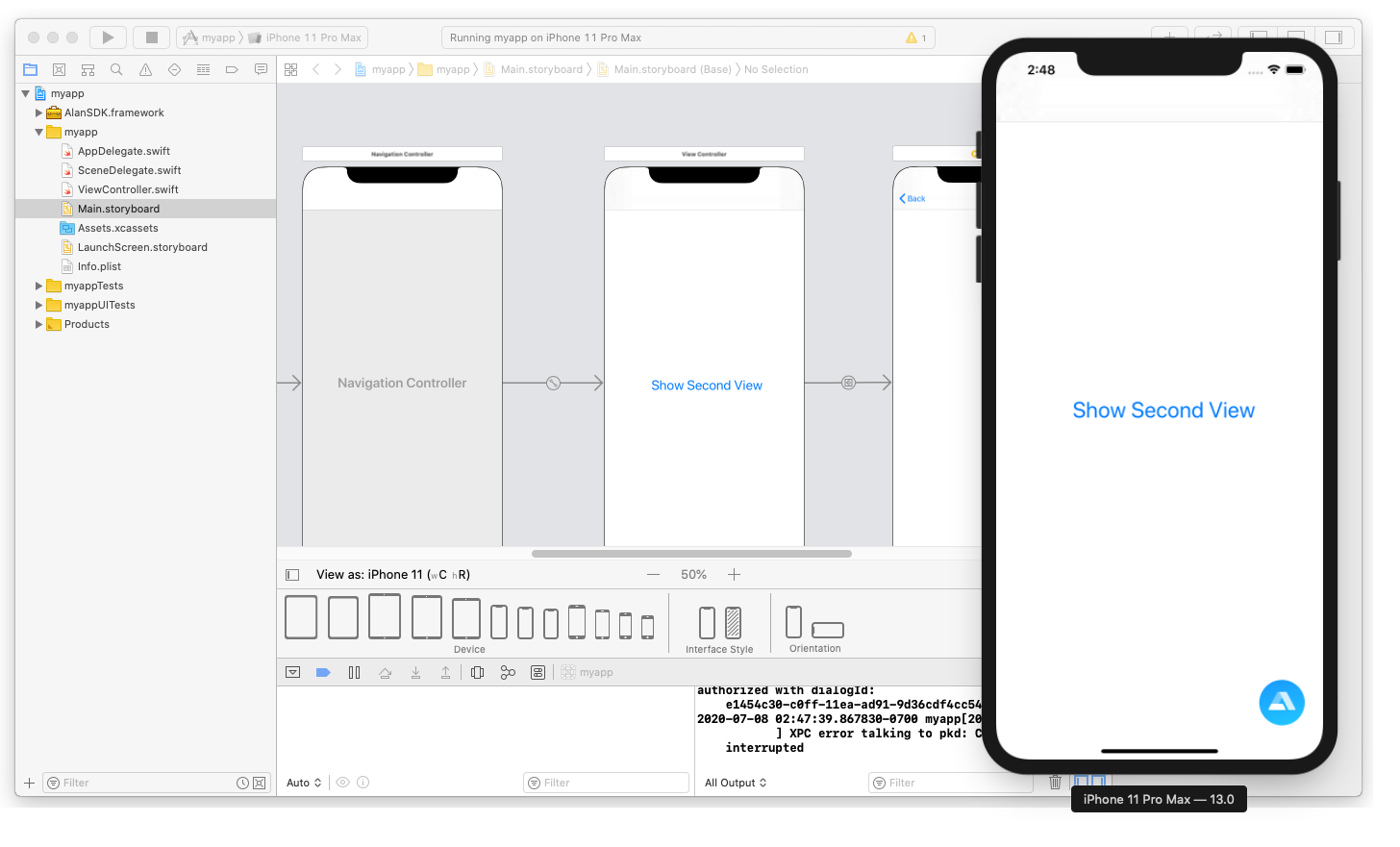
Run the app. When the app is launched on the simulator, tap the Show Second View button to navigate forward. In the second view, tap the Back button at the top to get back to the initial view.
Step 2: Add voice commands to navigate between views¶
We can navigate between views using the app’s UI. Now we need to add new commands to the dialog script to navigate between views with voice. In Alan AI Studio, open the project and in the code editor, add the following intents:
intent(`Navigate forward`, p => {
p.play({command: 'navigation', route: 'forward'});
p.play(`Navigating forward`);
});
intent(`Go back`, p => {
p.play({command: 'navigation', route: 'back'});
p.play(`Going back`);
});
Now, when we say one of these commands to the app, two things happen:
Alan AI sends the command provided in the intent to the app. To send the command, we need to specify a JSON object in the
p.playfunction. Here the object contains the command name and routing data:forwardorback.Alan AI plays back the action confirmation to us.
Step 3: Handle commands on the app side¶
When we say Navigate forward or Go back, Alan AI sends a command to the app. We need to handle this command on the app side and make sure an appropriate action is performed. Let’s add a handler for Alan AI’s events to our app.
In the
ViewController.swiftfile, inViewDidLoad(), call thesetupAlanEventHandler()function:ViewController.swift¶class ViewController: UINavigationController { /// Alan AI agentic interface fileprivate var button: AlanButton! override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() /// Set up the Alan AI agentic interface self.setupAlan() /// Set up a handler for events from Alan AI self.setupAlanEventHandler() } }
To the
ViewControllerclass, add the function itself. In this function, we add an observer for events coming from the dialog script. Once an event is received, thehandleEvent()function is invoked.ViewController.swift¶class ViewController: UINavigationController { fileprivate func setupAlanEventHandler() { /// Add an observer to get events from Alan AI NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(self, selector: #selector(self.handleEvent(_:)), name:NSNotification.Name(rawValue: "kAlanSDKEventNotification"), object:nil) } @objc func handleEvent(_ notification: Notification) { /// Get the user info object with JSON from Alan AI guard let userInfo = notification.userInfo, let jsonString = userInfo["jsonString"] as? String, let jsonData = jsonString.data(using: .utf8), let jsonObject = try? JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: jsonData, options: []) as? [String: Any], /// Get the object with the command data let commandObject = jsonObject["data"] as? [String: Any], /// Get the command name string let commandString = commandObject["command"] as? String else { return } /// Get the command name string if commandString == "navigation" { /// Get the route name string guard let routeString = commandObject["route"] as? String else { return } /// Forward command if routeString == "forward" { DispatchQueue.main.async { self.goForward() } } /// Back command else if routeString == "back" { DispatchQueue.main.async { self.goBack() } } } } }
And finally, to the
ViewControllerclass, add functions to navigate to the necessary view:goForward()andgoBack(). Have a look at thegoForward()function: here we use the ID of the segue we created in the first step.ViewController.swift¶class ViewController: UINavigationController { fileprivate func goForward() { /// Get the first view controller if let firstVC = self.viewControllers.first { /// Perform a segue to push the second view controller to the navigation stack. The segue is defined in the storyboard. firstVC.performSegue(withIdentifier: "goForward", sender: self) } } fileprivate func goBack() { /// Remove the second (last) view controller from the navigation stack self.popViewController(animated: true) } }
Let’s review the code above to see how it works. When the Navigation Controller is loaded, the setupAlanEventHandler() is invoked, and our app starts listening for events coming from Alan AI. Once an event, in our case, a command with a JSON object, is received from the dialog script, the handleEvent() function is triggered. The function processes the object and checks the value passed in the route key.
If the value is forward, the goForward() function is invoked, taking us to the second view. If the value is back, the goBack() function is invoked, and the initial view is displayed.
You can test it: run the app on the simulator, tap the Alan AI agentic interface and say: Navigate forward. The app will open the second view. Then say Go back, and the initial view will be displayed.
What you finally get¶
After you pass through this tutorial, you will have an iOS app with two views and will be able to send voice commands to navigate between them. You can get an example of such an app from the Alan AI GitHub to make sure you have set up your app correctly.
SwiftTutorial.part2.zip: XCode project of the app
SwiftTutorial.part2.js: voice commands used for this tutorial
What’s next?¶
Have a look at the next tutorial: Passing the app state to the dialog script.